Introduction
This documentation describes the pycopm tool hosted in https://github.com/cssr-tools/pycopm.
Concept
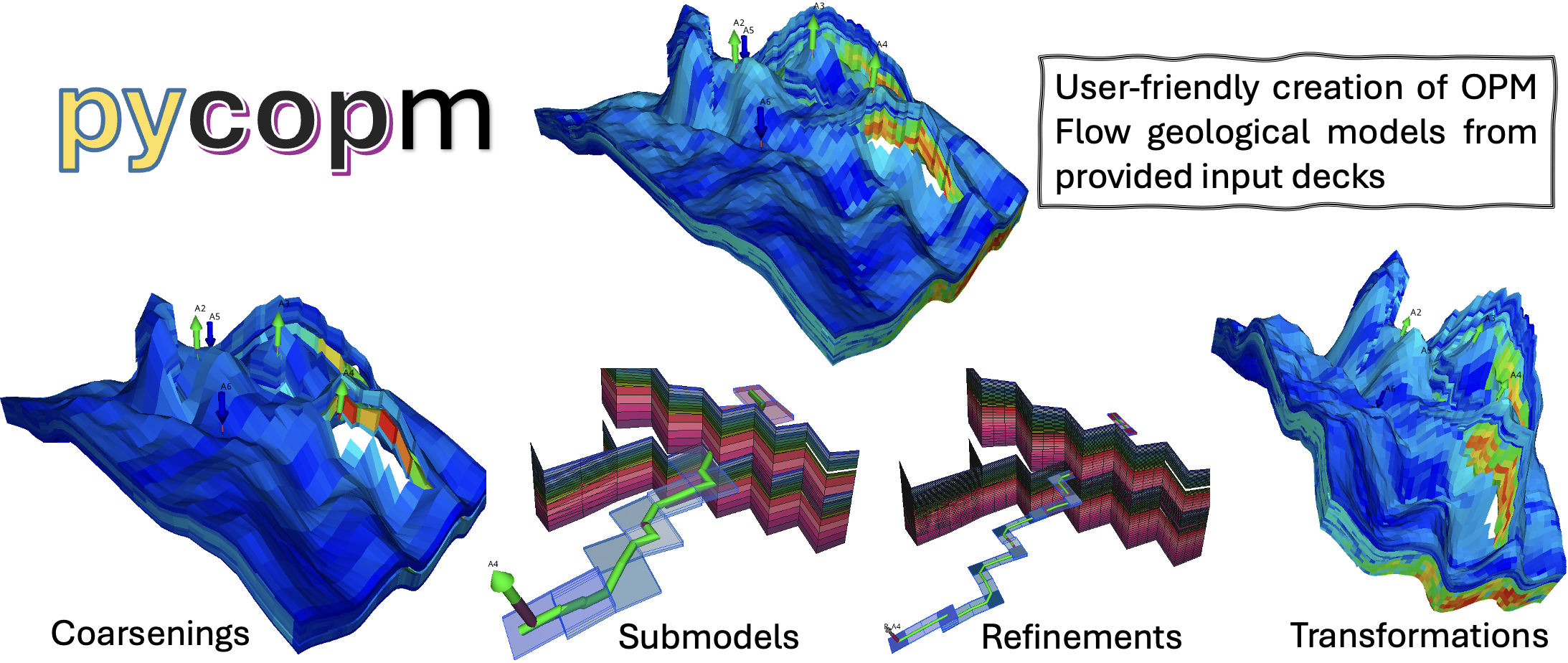
User-friendly creation of OPM Flow geological models from provided input decks with options for grid refinement, grid coarsening, submodels, and transformations including scalings, rotations, and translations.
Roadmap
In the initial development of the pycopm repository, the focus were two available models in opm-tests: norne and drogon, where the coarsened models were used to perform history matching studies using the Ensemble based reservoir tool ERT, via a configuration file.
The current development of pycopm focuses on creating models (i.e., all needed input files to run OPM Flow such as the grid) by only providing the OPM Flow input files (i.e., avoiding the manual work to create templates as it was done for drogon and norne). This allows for flexibility to adapt the generated decks in your favourite history matching/optimization tool (e.g., ERT, PET), as well as to test different approaches in diverse applications (e.g., proxy models, non-conforming grids, upscaling techniques).
Overview
The current implementation supports the following executable with the argument options:
pycopm -i name_of_input_file
where
- -i
The base name of the toml configuration file or the name of the deck, e.g., ‘DROGON.DATA’, (‘input.toml’ by default).
- -o
The base name of the output folder (‘.’ by default, i.e., the folder where pycopm is executed).
- -f
OPM Flow path to executable (e.g., /home/pycopm/build/opm-simulators/bin/flow), or just ‘flow’ if this was installed via binaries or if the folder where flow is built has been added to your path (‘flow’ by default).
- -m
Execute a dry run of the input deck to generate the static properties (‘prep’), generate only the modified files (‘deck’), only exectute a dry run on the generated model (‘dry’), ‘prep_deck’, ‘deck_dry’, or do all (‘all’) (‘prep_deck’ by default).
- -v
The location to extract the sub model which can be assigned by region values, e.g., ‘fipnum 2,4’ extracts the cells with fipnums equal to 2 or 4, by a polygon given the xy locations in meters, e.g., ‘xypolygon [0,0] [30,0] [30,30] [0,0]’, or by the name of the well and three different options for the neighbourhood: box, diamond, and diamondxy, where for box the i, j, and k interval around the connections are given, e.g., ‘welln box [-1,1] [-2,2] [0,3]’ results in a vicinity with 1 pm cell in the x direction, 2 pm cells in the y direction and only 3 cells in the k positive direction, while the diamond considers only the given number of cells around the well connections (e.g., ‘welln diamond 2’) and diamondxy it is restricted to the xy plane (’’ by default).
- -c
Level of coarsening in the x, y, and z dir (‘2,2,2’ by default; either use this flag or the -x, -y, and -z ones).
- -x
Array of x-coarsening, e.g., if the grid has 6 cells in the x direction, then ‘0,2,0,2,0,2,0’ would generate a coarsened model with 3 cells, while ‘0,2,2,2,2,2,0’ would generate a coarser model with 1 cell, i.e., 0 keeps the pilars while 2 removes them. As an alternative, the range of the cells to coarse can be given separate them by commas, e.g., ‘1:3,5:6’ generates a coarsened model with 3 cells where the cells with the first three and two last i indices are coarsened to one (’’ by default),
- -y
Array of y-coarsening, see the description for -x (’’ by default).
- -z
Array of z-coarsening, see the description for -x (’’ by default).
- -g
Level of grid refinement in the x, y, and z dir (’’ by default).
- -rx
Array of x-refinement, e.g., if the grid has 6 cells in the x direction, then ‘0,1,0,2,0,4’ would generate a refined model with 13 cells, while 0,0,0,1,0,0 would generate a refined model with 7 cells (’’ by default).
- -ry
Array of y-refinement, see the description for -rx (’’ by default).
- -rz
Array of z-refinement, see the description for -rx (’’ by default).
- -a
In coarsening, use ‘min’, ‘max’, or ‘mode’ to scale the actnum, e.g., ‘min’ makes the new coarser cell inactive if at least one cell is inactive, while ‘max’ makes it active it at least one cell is active (‘mode’ by default).
- -n
In coarsening, use ‘min’, ‘max’, or ‘mode’ to scale endnum, eqlnum, fipnum, fluxnum, imbnum, miscnum, multnum, opernum, pvtnum, rocknum, and satnum (‘mode’ by default).
- -s
In coarsening, use ‘min’, ‘max’, ‘mean’, or ‘pvmean’ to scale permx, permy, permz, poro, swatinit, disperc, thconr, and all mult(-)xyz (’’ by default, i.e., using the arithmetic average for permx/permy, harmonic average for permz, volume weighted mean for mult(-)xyz, and the pore volume weighted mean (‘pvmean’) for the rest).
- -p
In coarsening, set to ‘1’ to add the removed pore volume to the closest coarser cells, while in submodels ‘1’ adds the porv from outside on the boundary of the submodel, ‘2’ adds the corner regions (e.g., below the mini and minj from the input model) to the corners in the submodel, ‘3’ distributes the porv uniformly along the boundary, and ‘4’ distributes it on the whole submodel (‘0’ by default, i.e., no porv correction).
- -q
Adjust the pv to the initial FGIP and FOIP from the input deck; use this option only for systems with initial oil, gas, and water, e.g., norne or drogon, but no in Smeaheia (‘0’ by default, ‘1’ to enable).
- -t
In coarsening, write and use upscaled transmissibilities by (‘1’) armonic averaging and summing the transmissibilities in the corresponding coarsening direction and (‘2’) scaling the face transmissibily on the coarse faces (‘0’ by default, i.e., transmissibilities are not used).
- -r
Remove CONFACT and KH from COMPDAT (‘1’) and also remove PEQVR (‘2’) (ITEM 13, the last entry) to compute the well transmisibility connections internally in OPM Flow using the grid properties (‘2’ by default; set to ‘0’ to not remove).
- -j
In coarsening, tuning parameter to avoid creation of neighbouring connections in the coarsened model where there are discontinuities between cells along the z direction, e.g., around faults (’’ by default, i.e., nothing corrected; if need it, try with values of the order of 1).
- -w
Name of the generated deck (’’ by default, i.e., the name of the input deck plus _PYCOPM.DATA).
- -l
Added text before each generated .INC (‘PYCOPM_’ by default, i.e., the modified porv is saved in PYCOPM_PORV.INC; set to ‘’ to generate PORV.INC, PERMX.INC, etc).
- -e
Use ‘utf8’ or ‘ISO-8859-1’ encoding to read the deck (‘ISO-8859-1’ by default).
- -ijk
Given i,j,k indices in the input model, return the modified i,j,k corresponding positions (’’ by default; if not empty, e.g., ‘1,2,3’, then there will not be generation of modified files, only the i,j,k mapped indices in the terminal).
- -d
Options to transform the x,y,z coordinates: ‘translate [10,-5,4]’ adds the values in meters to the coordinates, ‘scale [1,2,3]’ multiplies the coordinates by the given values respectively, and ‘rotatexy 45’ applies a rotation in degrees in the xy plane (rotatexz and rotateyz applies a rotation around the y and x axis respectively) (’’ by default).
- -explicit
Set to 1 to explicitly write the cell values in the SOLUTION section in the deck (‘0’ by default).
- -dual
Set the criterium to differentiate net and non-net in coarsening using a static variable, e.g., ‘poro <= 0.1’ (’’ by default).